The 8 steps methodology overview
Introduction: From Risk Demand to Actionable Insights
Risk management is not just about identifying threats. It's about taking structured, measurable actions to mitigate, transfer, accept, or avoid them.
The CSFaaS Risk Demand workflow follows a structured approach, ensuring risks are properly assessed, categorised, and addressed with remediation plans.
Below is an example of a completed risk demand, illustrating how risks are identified, classified, and connected to mitigation actions and remediation plans.
📊 Example of a Completed Risk Demand Analytics View:
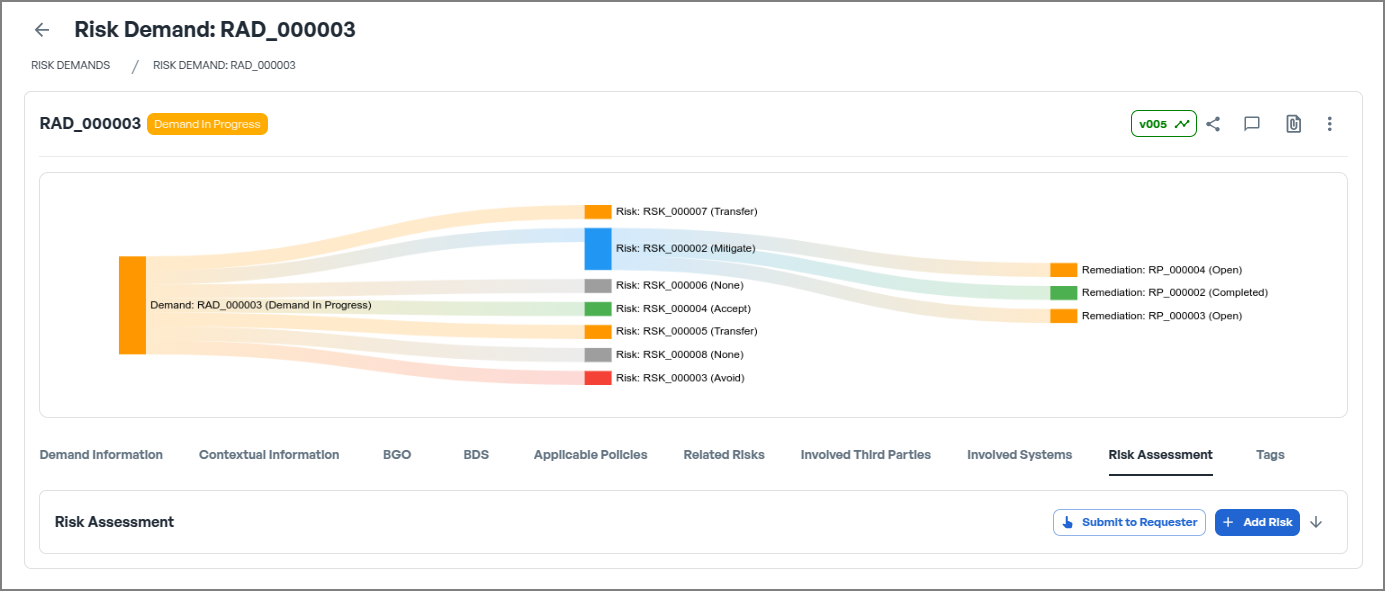
This visual representation showcases:
- Risk Identification – The source and classification of the risk.
- Risk Categorisation – How risks are analysed, from origin to threat actors.
- Risk Treatment Decisions – Whether a risk is mitigated, accepted, transferred, or avoided.
- Remediation Actions – Steps taken to address and resolve the risk.
With this structured approach, the 8-step methodology ensures that all cybersecurity risks are assessed, tracked, and aligned with organisational risk appetite.
The methodology is divided into the following 8 steps.
Step 1: Add a Risk
Define and document risks, including their origin, context, and initial classification.
Step 2: Define the risk profile
To establish a detailed risk profile, analyse and categorise risks based on:
- Security Domain
- Business Attribute
- Risk Category
- Threat origin
- Threat actors
- Threat actors motivation
- Threat vectors
- STRIDE definition
- Threat actions
- Victim Quantification
- Other information (text box).
Step 3: Assess the Inherent Risk
Evaluate the risk in its raw state, without considering any existing mitigation measures. This involves:
- Strengths Analysis
- Weaknesses Analysis
- Opportunities Analysis
- Impact Type
Based on this assessment, define:
- The likelihood level (considering Threats & Vulnerabilities).
- The risk exposure using the formula: Likelihood × Impact.
Step 4: Assess the Current Risk
Evaluate the risk level in the context before applying existing controls and mitigation measures, based on:
- Strengths Analysis
- Weaknesses Analysis
- Opportunities Analysis
- Impact Type
Based on this assessment, define:
- The likelihood level (considering Threats & Vulnerabilities).
- The risk exposure using the formula: Likelihood × Impact.
Step 5: Recommend Controls
Identify and propose measures to address vulnerabilities and reduce the risk to an acceptable level.
Step 6: Assess the Target Risk
Define the desired residual risk level aligned with the organisation's risk tolerance and appetite, based on:
- Strengths Analysis
- Weaknesses Analysis
- Opportunities Analysis
- Impact Type
Based on this assessment, define:
- The likelihood level (considering Threats & Vulnerabilities).
- The risk exposure using the formula: Likelihood × Impact.
Step 7: Submit for Risk Response
Formalise and submit the risk assessment findings and recommended controls for stakeholder approval.
Step 8: Provide a Risk Response
Implement approved risk response measures, monitor their effectiveness, and document results.
This methodology ensures a consistent, transparent, and repeatable approach to managing cybersecurity risks across systems, third parties, and organisational processes.
The integration of SWOT analysis into the methodology provides both strategic insight and practical direction, ensuring informed decision-making throughout the risk management lifecycle.